Human parasites are represented by several groups, one of which is protozoa. Capable of causing disease of varying degrees of severity, these microorganisms are not as easy to diagnose as groups with a more complex organization. For convenience, in the article they are presented in a table with the main characteristics.
Characteristic
Among the simplest are organisms with a primitive organization, grouped together in the phylum Protozoa. It has more than 15, 000 species, and some of them lead a parasitic lifestyle in the human body. All of them are characterized by small sizes, they can only be seen with a microscope and cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Many of the simplest parasites are extremely primitive in structure. Once in the host's body, they begin to multiply. Sometimes this is done by splitting in half, sometimes by multiple splitting. In the latter case, the disease develops rapidly, symptoms quickly appear, which can sometimes even cause the death of a person.
Features of biology
The organism of protozoan human parasites consists of two main parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm, in which all other organelles are located. The core can be one or more.
Protozoa have the ability to form a cyst in unfavorable environmental conditions. This allows them to remain viable for long periods of time, remaining motionless and deprived of nutrients. Once conditions return to normal, the cyst envelope is destroyed and the microorganism continues to function normally. Encystation also allows parasites to successfully spread from organism to organism.
All protozoa are divided into several categories based on their anatomy, mode of movement and other characteristics:
- flagella;
- sarcode
- sporozoa
- ciliates.
Within each group there are species for which humans are the intermediate or definitive host.
main types
Parasites of the Protozoa species cause many diseases and parasitize in various organs. For convenience, they are presented in the table.
| Surname | Infected body parts | method of infection | symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Balantidia | lower intestine | Eating undercooked pork or water with cysts | Balantidiasis is often accompanied by diarrhea. White mucus and bloody discharge appear in the feces. The colon mucosa ulcerates and in such cases bleeding may increase. With the progression of the disease, exhaustion of a person occurs, which in rare cases can lead to death. |
| mouth amoeba | Oral cavity, periodontal pockets, dental plaque | A person becomes infected by kissing a carrier, using dirty dishes, and eating contaminated food. | It rarely affects people who do not have pathological lesions in the oral cavity. In inflammation, the oral amoeba feeds on epithelium, microbes, leukocytes and erythrocyte cells. Can cause periodontitis. |
| dysenteric amoeba | Through the bloodstream, it enters the lungs, liver, heart, genitals, and kidneys. Settles in the intestinal lumen | Ingestion with food or water | In some cases, the disease is asymptomatic. If the dysentery amoeba attacks the intestinal walls, the pathogenic stage begins. It is characterized by colitis, tissue necrosis, liver damage, abscesses can appear. Very serious consequences cause metastases in the brain and other organs. Possible fatal outcome. Sometimes the disease takes a relapsing course. Self-healing rarely occurs |
| Giardia in the gut | duodenum and bile ducts. | oral route | Giardia adhere to the mucosal epithelium and interfere with nutrient absorption. Inflammation of the mucous membranes and constant diarrhea develop. When the infection covers the bile ducts, yellowing of the skin occurs. Some people develop immunity to intestinal Giardia, particularly in countries with tropical climates. |
| Trichomonas vaginalis | In women - on the vaginal mucosa, in men - in the epidermis of the prostate and in the urethra | During sexual intercourse, as well as during childbirth from mother to child | Trichomoniasis is manifested by foamy discharge, itching and burning on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, pain during sex, the appearance of bloody discharge from the urethra, etc. A complication of trichomoniasis is inflammation of the vulva due to the activity of protozoa, cystitis, prostatitis and infertility |
| Trypanosoma brussei | Cerebrospinal fluid and the brain | After being bitten by a tsetse fly, which is an intermediate host | Begins with fever and swollen lymph nodes, progresses to apathy, irresistible need for sleep, muscle paralysis and exhaustion. If left untreated, coma and death will occur. |
| Cutaneous Leishmania | Contact with a sick person or animal | On the skin, mostly on the face or hands | The incubation period lasts from 2 months to 5 years, after which a brownish dense node appears at the site of the insect bite. It increases, and then a purulent ulcer opens in its place. The disease lasts up to several years, and then the final scarring of the wounds occurs. Complications can include diseases of the heart, kidneys and adrenal glands. |
| toxoplasma | Infected pets, mainly cats, sometimes infection occurs when eating food containing protozoa | liver, heart, eyes, brain | In the congenital form - multiple pathologies of fetal development, death in infancy, mental retardation, multiple infections. Acquired toxoplasmosis causes high fever, enlarged liver, headache, vomiting, convulsions. Often takes a chronic course with increased fatigue and eye damage. Rarely occurs in a latent form |
| Isospora | From an infected person with fecal-oral transmission | epithelium of the small intestine | The incubation period is about 10 days. Then the body temperature rises, vomiting and diarrhea appear. The disease is acute for a week or two, then recovery occurs |
| cryptosporidia | oral route | epithelial tissue of the intestine | Incubation lasts about a week, then diarrhea begins, possibly with inclusions of spotting. The stomach may hurt, fever appears, signs of dehydration are possible. With insufficient immune status of the patient, the infection can affect other organs: lungs, pancreas, stomach, etc. |
Are worms the simplest
Sometimes you can hear the phrase that the patient is infected with the simplest worms. It must be understood that protozoa are exclusively unicellular microorganisms that, in extreme cases, organize colonies. But they are never multicellular like worms and helminths.
In protozoa, all processes take place inside the cell cytoplasm and nuclei, while in worms the anatomical organization is much more complicated: they have differentiated organs that perform special physiological functions. Therefore, it is fundamentally wrong to classify worms as protozoa.
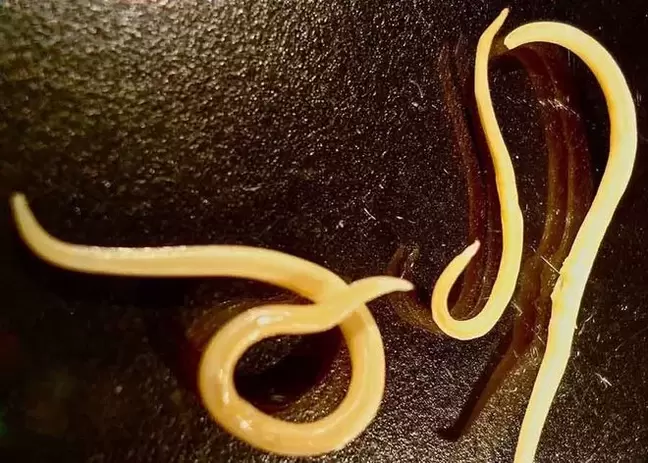

Sometimes helminths are called the simplest parasites compared to insects: bugs, lice, etc. , since the latter are much higher on the evolutionary ladder. In this interpretation, the designation of worms as protozoa is permitted.